Insights
Understanding Customer Lifetime Value for D2C Brands
Jan 24, 2025

Abhimanyu Atri
Marketing Associate




Performance Marketing and CLV
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a crucial metric for Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) brands in the digital age. It represents the total revenue or profit a business can expect from a single customer throughout its relationship. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) has emerged as a critical metric in understanding long-term profitability, while Performance Marketing ensures that every marketing dollar is tied to measurable results.
What Is Performance Marketing?
Performance Marketing is a branch of digital marketing where advertisers pay only for specific, measurable actions—such as clicks, leads, or sales—rather than traditional, impression-based fees. You can read more about Performance Marketing in our comprehensive guide here.
Importance of Customer Lifetime Value for Performance Marketing
Understanding and optimizing CLV enhances campaign profitability and informs marketing strategies that drive sustainable growth.
Long-term Profitability: CLV provides insights into how much a customer is worth over time, allowing businesses to focus on retaining high-value customers rather than just acquiring new ones.
Marketing Efficiency: By understanding CLV, brands can allocate marketing budgets more effectively, targeting channels that yield the highest returns on investment.
Customer Segmentation: Analyzing CLV helps identify different customer segments, enabling personalized marketing strategies that enhance engagement and loyalty.
Understanding Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
What Is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?
Definition and Importance

Figure 1. What is Customer Lifetime Value
CLV measures the projected net profit a business can expect from a single customer over the entire duration of their relationship. Unlike one-off metrics such as average order value (AOV) or immediate sales, CLV takes a longitudinal perspective, accounting for repeat purchases, retention, and referrals.
How Is CLV Calculated?
Basic Formula
A commonly cited basic formula for CLV is:
CLV= (Average Order Value×Purchase Frequency×Gross Margin)/Churn Rate
Average Order Value (AOV): The average amount spent per transaction by the customer.
Purchase Frequency: How often a customer typically buys within a given period.
Gross Margin: (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) ÷ Revenue.
Churn Rate: The rate at which customers stop buying from you over a certain period.
What Are the Key Components That Contribute to CLV?

Figure 2. Factors Contributing to CLV
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The amount spent to convert a lead into a paying customer. High CAC eats into margins and lowers net CLV if not controlled. Aim for a CLV:CAC ratio of 3:1 or higher, indicating that the lifetime value of a customer should be at least three times the cost of acquiring them.
Gross Margin per Customer The difference between the revenue generated and the cost of goods sold (COGS). Higher margins generally yield a higher CLV.
Retention Rate and Churn Rate: Retention Rate is the percentage of customers who remain active over a given time. The Churn Rate measures how quickly customers drop off. Small increases in retention can lead to significant boosts in CLV. Loyalty programs and personalized communication keep customers engaged boosting retention rates.
Referral Value Existing customers often refer new customers through word-of-mouth or referral programs. Incorporating referral value adds another dimension to CLV, especially for subscription and SaaS models.
Customer Satisfaction: High satisfaction often correlates with repeat business and positive word-of-mouth.
Lifecycle Stage: Newly acquired customers may have a lower CLV than long-standing, loyal customers.
How Does CLV Vary Across Different Industries?
Industry-specific factors—like average margins, customer loyalty norms, and seasonality—can significantly impact CLV benchmarks. For instance, luxury fashion may have a lower purchase frequency but higher AOV, whereas fast-moving consumer goods might see a more frequent but lower-value transaction pattern.
E-commerce: Physical product-based businesses see variations in CLV due to shipping costs, return rates, and product categories.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C): Often leverages brand loyalty and unique product offerings, leading to potentially higher repeat purchases.
SaaS: Subscription-based models often rely on a Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) structure, where CLV is closely tied to retention (churn rate).
Subscription Services: Like SaaS, but may also include membership boxes (e.g., beauty, food, or pet supplies). Consistent retention is key.
The Role of CLV in Performance Marketing
Why Is the Intersection of Performance Marketing and CLV Important for D2C Brands?
D2C brands thrive on brand equity and customer loyalty. Unlike traditional retail models, D2C businesses often have:
Direct Access to Customer Data: Helps in building detailed customer profiles.
Lower Overhead Costs: Potentially lower CAC if marketing is optimized.
High Competition: The crowded digital marketplace makes retention and loyalty essential.
Performance marketing maximizes CLV by focusing on measurable actions that lead to sales. By aligning performance marketing objectives with CLV, D2C brands can:
Target High-Value Customers: Use data-driven insights to refine messaging and campaigns aimed at attracting customers with higher lifetime value.
Measure Campaign Effectiveness: By incorporating CLV into ROI calculations, brands can evaluate the long-term success of their marketing efforts.
Optimize Marketing Spend: Allocate budgets to channels and campaigns that attract higher-value customers.
Refine Messaging: Tailor ads and content to customer segments with the highest long-term value.
Drive Sustainable Growth: Focus less on volume at any cost and more on attracting loyal, profitable customers.
What Is the Relationship Between CLV and Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)?
A hallmark metric in performance marketing is the CLV:CAC ratio. Ideally, businesses aim for a ratio of 3:1 or higher.
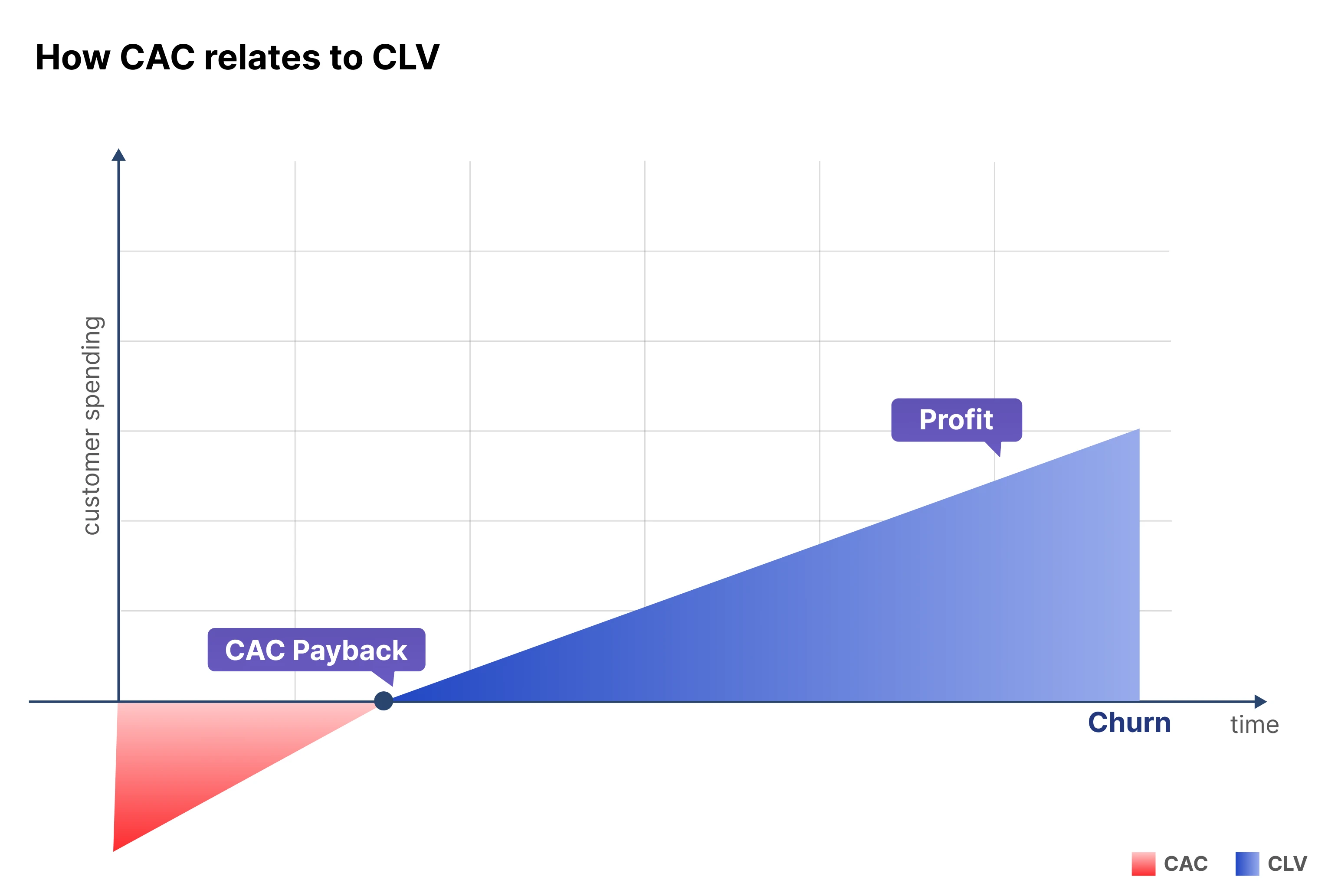
Figure 3. CAC to CLV Relation
Strategies to Optimize This Ratio
Reduce CAC:
Use highly targeted advertising campaigns to attract prospects more likely to convert.
Invest in content marketing and SEO for lower-cost, sustainable acquisition channels.
Increase CLV:
Implement loyalty programs that encourage repeat purchases.
Focus on cross-selling and upselling to boost average order value.
How Does CLV Influence Return on Investment (ROI) in Marketing Campaigns?
Measuring ROI with CLV Considerations
When evaluating marketing campaigns, factoring in CLV provides a long-term lens. A campaign that appears unprofitable initially (due to high CAC) could yield substantial returns over time if customers remain loyal and keep purchasing.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term ROI Implications
Short-Term: Typically focuses on immediate conversions and revenue.
Long-Term: Encompasses the entire lifecycle of a customer, from the first sale to subsequent purchases, referrals, and brand advocacy.
Integrating CLV into Performance Marketing Strategies
How to Incorporate CLV into Budgeting and Campaign Planning?
Use Historical Data: Analyze past purchase behavior and churn rates to forecast future CLV.
Allocate Budgets by CLV Segments: If a particular segment has a higher average CLV, consider aggressively targeting that segment with higher ad spend.
Optimize for Profit, Not Just Volume: Balance volume and profitability by focusing on channels that bring in higher-value customers, even if cost-per-acquisition is slightly higher.
What Metrics Should Performance Marketers Track Alongside CLV?
Average Order Value (AOV): Tracks immediate revenue per transaction.
Conversion Rate (CR): Measures how effectively your campaigns convert leads to customers.
Lifetime Conversion Rate: Reflects how many conversions a single customer will make over their entire relationship.
Retention Rate: Indicates how effectively you retain customers over time.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) or Net Promoter Score (NPS): While not directly tied to revenue, high satisfaction often correlates with higher CLV.
How Can CLV Segmentation Enhance Targeting and Personalization?
Segmenting customers by CLV allows for tailored marketing:
High-CLV Customers: Provide exclusive offers, priority support, and loyalty perks.
Mid-CLV Customers: Encourage upsells or cross-sells to move them into the high-CLV bracket.
Low-CLV Customers: Consider optimizing retention strategies or re-evaluating if the acquisition of these segments is worthwhile long-term.
Personalized ads and email campaigns that reference previous purchases, browsing history, or customer interests can significantly improve engagement and drive repeat business.
Measuring and Analyzing CLV
What Are The Best Tools and Technologies for Tracking and Analyzing CLV?
CRM Systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot):
Centralize customer data, track interactions, and generate lifetime value metrics.
Pros: Integrations with marketing automation, robust reporting.
Cons: Can be expensive and complex to set up for small businesses.
Analytics Platforms (e.g., Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics):
Track user behavior from acquisition to conversion.
Pros: Widely used, strong user community, free options (Google).
Cons: Limited direct CLV calculations, requiring custom setups.
Specialized CLV Tools (e.g., Custora, Zaius):
Built specifically for customer-centric analytics and predictive modeling.
Pros: Advanced forecasting, cohort analysis, segmentation.
Cons: Higher cost and a learning curve for complex features.
How to Use Data Analytics to Predict and Improve CLV?
Predictive Modeling: Use regression analysis or machine learning algorithms to forecast how changes in purchase frequency or AOV could affect CLV.
Cohort Analysis: Group customers by their acquisition date or behavior patterns to identify retention trends over time.
A/B Testing: Test new marketing tactics on smaller segments to see how they influence short-term purchases and forecasted CLV.
What Are The Common Challenges in Measuring CLV, and How to Overcome Them?
Data Accuracy and Integration Issues
Solution: Implement robust data hygiene practices, use unified customer databases, and establish consistent data tracking protocols.
Multi-Channel Attribution
Challenge: Customers may interact with multiple touchpoints before purchasing.
Solution: Employ multi-touch attribution models in analytics tools to capture the role of each channel in influencing conversion.Customer Behavior Complexity
Solution: Use advanced segmentation and machine learning to identify patterns, rather than relying solely on averages.
What Tactics Can Increase Customer Retention?
Email Marketing
Personalized email campaigns (e.g., product recommendations, anniversary offers).
Automated re-engagement campaigns targeting inactive customers.
Loyalty Programs
Reward points, tiered memberships, and exclusive events.
Gamification to keep customers engaged over time.
Retargeting Strategies
Use paid ads on platforms like Facebook and Google to re-engage site visitors and past buyers with relevant offers.
Content Marketing and Community Building
Blogs, videos, and forums to add value beyond the product itself.
Encourages word-of-mouth and brand advocacy.
Cross Selling
Identifying Opportunities: Data on past purchases and browsing behavior can indicate which products or services a customer is likely to buy next.
Effective Implementation:
Timing: Offer complementary items immediately post-purchase or when usage data suggests readiness.
Personalization: Highlight product bundles that match the customer’s interests.
Conclusion
For D2C brands, understanding and optimizing Customer Lifetime Value is essential for driving growth and profitability. By integrating CLV into performance marketing strategies, businesses can enhance customer engagement, improve retention rates, and ultimately achieve sustainable success in the competitive digital marketplace.
Incorporating these insights into your business strategy will not only help in attracting and retaining valuable customers but also position your brand as an expert in maximizing customer relationships.
Performance Marketing and CLV
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a crucial metric for Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) brands in the digital age. It represents the total revenue or profit a business can expect from a single customer throughout its relationship. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) has emerged as a critical metric in understanding long-term profitability, while Performance Marketing ensures that every marketing dollar is tied to measurable results.
What Is Performance Marketing?
Performance Marketing is a branch of digital marketing where advertisers pay only for specific, measurable actions—such as clicks, leads, or sales—rather than traditional, impression-based fees. You can read more about Performance Marketing in our comprehensive guide here.
Importance of Customer Lifetime Value for Performance Marketing
Understanding and optimizing CLV enhances campaign profitability and informs marketing strategies that drive sustainable growth.
Long-term Profitability: CLV provides insights into how much a customer is worth over time, allowing businesses to focus on retaining high-value customers rather than just acquiring new ones.
Marketing Efficiency: By understanding CLV, brands can allocate marketing budgets more effectively, targeting channels that yield the highest returns on investment.
Customer Segmentation: Analyzing CLV helps identify different customer segments, enabling personalized marketing strategies that enhance engagement and loyalty.
Understanding Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
What Is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?
Definition and Importance

Figure 1. What is Customer Lifetime Value
CLV measures the projected net profit a business can expect from a single customer over the entire duration of their relationship. Unlike one-off metrics such as average order value (AOV) or immediate sales, CLV takes a longitudinal perspective, accounting for repeat purchases, retention, and referrals.
How Is CLV Calculated?
Basic Formula
A commonly cited basic formula for CLV is:
CLV= (Average Order Value×Purchase Frequency×Gross Margin)/Churn Rate
Average Order Value (AOV): The average amount spent per transaction by the customer.
Purchase Frequency: How often a customer typically buys within a given period.
Gross Margin: (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) ÷ Revenue.
Churn Rate: The rate at which customers stop buying from you over a certain period.
What Are the Key Components That Contribute to CLV?

Figure 2. Factors Contributing to CLV
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The amount spent to convert a lead into a paying customer. High CAC eats into margins and lowers net CLV if not controlled. Aim for a CLV:CAC ratio of 3:1 or higher, indicating that the lifetime value of a customer should be at least three times the cost of acquiring them.
Gross Margin per Customer The difference between the revenue generated and the cost of goods sold (COGS). Higher margins generally yield a higher CLV.
Retention Rate and Churn Rate: Retention Rate is the percentage of customers who remain active over a given time. The Churn Rate measures how quickly customers drop off. Small increases in retention can lead to significant boosts in CLV. Loyalty programs and personalized communication keep customers engaged boosting retention rates.
Referral Value Existing customers often refer new customers through word-of-mouth or referral programs. Incorporating referral value adds another dimension to CLV, especially for subscription and SaaS models.
Customer Satisfaction: High satisfaction often correlates with repeat business and positive word-of-mouth.
Lifecycle Stage: Newly acquired customers may have a lower CLV than long-standing, loyal customers.
How Does CLV Vary Across Different Industries?
Industry-specific factors—like average margins, customer loyalty norms, and seasonality—can significantly impact CLV benchmarks. For instance, luxury fashion may have a lower purchase frequency but higher AOV, whereas fast-moving consumer goods might see a more frequent but lower-value transaction pattern.
E-commerce: Physical product-based businesses see variations in CLV due to shipping costs, return rates, and product categories.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C): Often leverages brand loyalty and unique product offerings, leading to potentially higher repeat purchases.
SaaS: Subscription-based models often rely on a Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) structure, where CLV is closely tied to retention (churn rate).
Subscription Services: Like SaaS, but may also include membership boxes (e.g., beauty, food, or pet supplies). Consistent retention is key.
The Role of CLV in Performance Marketing
Why Is the Intersection of Performance Marketing and CLV Important for D2C Brands?
D2C brands thrive on brand equity and customer loyalty. Unlike traditional retail models, D2C businesses often have:
Direct Access to Customer Data: Helps in building detailed customer profiles.
Lower Overhead Costs: Potentially lower CAC if marketing is optimized.
High Competition: The crowded digital marketplace makes retention and loyalty essential.
Performance marketing maximizes CLV by focusing on measurable actions that lead to sales. By aligning performance marketing objectives with CLV, D2C brands can:
Target High-Value Customers: Use data-driven insights to refine messaging and campaigns aimed at attracting customers with higher lifetime value.
Measure Campaign Effectiveness: By incorporating CLV into ROI calculations, brands can evaluate the long-term success of their marketing efforts.
Optimize Marketing Spend: Allocate budgets to channels and campaigns that attract higher-value customers.
Refine Messaging: Tailor ads and content to customer segments with the highest long-term value.
Drive Sustainable Growth: Focus less on volume at any cost and more on attracting loyal, profitable customers.
What Is the Relationship Between CLV and Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)?
A hallmark metric in performance marketing is the CLV:CAC ratio. Ideally, businesses aim for a ratio of 3:1 or higher.

Figure 3. CAC to CLV Relation
Strategies to Optimize This Ratio
Reduce CAC:
Use highly targeted advertising campaigns to attract prospects more likely to convert.
Invest in content marketing and SEO for lower-cost, sustainable acquisition channels.
Increase CLV:
Implement loyalty programs that encourage repeat purchases.
Focus on cross-selling and upselling to boost average order value.
How Does CLV Influence Return on Investment (ROI) in Marketing Campaigns?
Measuring ROI with CLV Considerations
When evaluating marketing campaigns, factoring in CLV provides a long-term lens. A campaign that appears unprofitable initially (due to high CAC) could yield substantial returns over time if customers remain loyal and keep purchasing.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term ROI Implications
Short-Term: Typically focuses on immediate conversions and revenue.
Long-Term: Encompasses the entire lifecycle of a customer, from the first sale to subsequent purchases, referrals, and brand advocacy.
Integrating CLV into Performance Marketing Strategies
How to Incorporate CLV into Budgeting and Campaign Planning?
Use Historical Data: Analyze past purchase behavior and churn rates to forecast future CLV.
Allocate Budgets by CLV Segments: If a particular segment has a higher average CLV, consider aggressively targeting that segment with higher ad spend.
Optimize for Profit, Not Just Volume: Balance volume and profitability by focusing on channels that bring in higher-value customers, even if cost-per-acquisition is slightly higher.
What Metrics Should Performance Marketers Track Alongside CLV?
Average Order Value (AOV): Tracks immediate revenue per transaction.
Conversion Rate (CR): Measures how effectively your campaigns convert leads to customers.
Lifetime Conversion Rate: Reflects how many conversions a single customer will make over their entire relationship.
Retention Rate: Indicates how effectively you retain customers over time.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) or Net Promoter Score (NPS): While not directly tied to revenue, high satisfaction often correlates with higher CLV.
How Can CLV Segmentation Enhance Targeting and Personalization?
Segmenting customers by CLV allows for tailored marketing:
High-CLV Customers: Provide exclusive offers, priority support, and loyalty perks.
Mid-CLV Customers: Encourage upsells or cross-sells to move them into the high-CLV bracket.
Low-CLV Customers: Consider optimizing retention strategies or re-evaluating if the acquisition of these segments is worthwhile long-term.
Personalized ads and email campaigns that reference previous purchases, browsing history, or customer interests can significantly improve engagement and drive repeat business.
Measuring and Analyzing CLV
What Are The Best Tools and Technologies for Tracking and Analyzing CLV?
CRM Systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot):
Centralize customer data, track interactions, and generate lifetime value metrics.
Pros: Integrations with marketing automation, robust reporting.
Cons: Can be expensive and complex to set up for small businesses.
Analytics Platforms (e.g., Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics):
Track user behavior from acquisition to conversion.
Pros: Widely used, strong user community, free options (Google).
Cons: Limited direct CLV calculations, requiring custom setups.
Specialized CLV Tools (e.g., Custora, Zaius):
Built specifically for customer-centric analytics and predictive modeling.
Pros: Advanced forecasting, cohort analysis, segmentation.
Cons: Higher cost and a learning curve for complex features.
How to Use Data Analytics to Predict and Improve CLV?
Predictive Modeling: Use regression analysis or machine learning algorithms to forecast how changes in purchase frequency or AOV could affect CLV.
Cohort Analysis: Group customers by their acquisition date or behavior patterns to identify retention trends over time.
A/B Testing: Test new marketing tactics on smaller segments to see how they influence short-term purchases and forecasted CLV.
What Are The Common Challenges in Measuring CLV, and How to Overcome Them?
Data Accuracy and Integration Issues
Solution: Implement robust data hygiene practices, use unified customer databases, and establish consistent data tracking protocols.
Multi-Channel Attribution
Challenge: Customers may interact with multiple touchpoints before purchasing.
Solution: Employ multi-touch attribution models in analytics tools to capture the role of each channel in influencing conversion.Customer Behavior Complexity
Solution: Use advanced segmentation and machine learning to identify patterns, rather than relying solely on averages.
What Tactics Can Increase Customer Retention?
Email Marketing
Personalized email campaigns (e.g., product recommendations, anniversary offers).
Automated re-engagement campaigns targeting inactive customers.
Loyalty Programs
Reward points, tiered memberships, and exclusive events.
Gamification to keep customers engaged over time.
Retargeting Strategies
Use paid ads on platforms like Facebook and Google to re-engage site visitors and past buyers with relevant offers.
Content Marketing and Community Building
Blogs, videos, and forums to add value beyond the product itself.
Encourages word-of-mouth and brand advocacy.
Cross Selling
Identifying Opportunities: Data on past purchases and browsing behavior can indicate which products or services a customer is likely to buy next.
Effective Implementation:
Timing: Offer complementary items immediately post-purchase or when usage data suggests readiness.
Personalization: Highlight product bundles that match the customer’s interests.
Conclusion
For D2C brands, understanding and optimizing Customer Lifetime Value is essential for driving growth and profitability. By integrating CLV into performance marketing strategies, businesses can enhance customer engagement, improve retention rates, and ultimately achieve sustainable success in the competitive digital marketplace.
Incorporating these insights into your business strategy will not only help in attracting and retaining valuable customers but also position your brand as an expert in maximizing customer relationships.
Share:
Share:
Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!

Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!

Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!

Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!






