Customer Data and Analytics
Track your visitor’s event correctly to improve RoAS of the Ad Campaigns
Mar 29, 2024

Anil Bains
Founder and CEO




In data-driven marketing, the smallest trackable unit of visitor interaction is called an event. Events are user actions that are tracked, measured, and stored to evaluate the effectiveness of a performance marketing campaign. Combining multiple events across time helps businesses track user journeys across the website. Some of the common events tracked include:
Social Interactions: when users engage by sharing, liking or commenting on social media content related to the campaign
Impressions: when an advertisement is displayed to a visitor
Clicks: when a user clicks on an advertisement
Add to Cart: when a user adds a product to the shopping cart
Conversions: when a user takes a desired action like making a purchase or submitting a form
Once an event is identified and triggered, the tracking code sends the tracking data with metadata like event category, event name, timestamp, and other related attributes. The tracking of these events can occur either on the client side or the server side. While it may seem convenient to do everything on the client or the server side, there are drawbacks to both methods. The choice between client-side and server-side tracking depends on the type of events being tracked. One approach may be more suitable than the other based on needs. Also, while some of the events are available on the client side, issues like ad blockers make tracking events on the server a better option.
Client vs. server tracking: what’s the difference?
The client initiates requests for resources like files or web pages, acting as the consumer of information. Conversely, the server's responsibility is to respond to these requests by providing the requested data or content.
The client represents the user-facing application or interface, such as a web browser (Firefox, Chrome) running on a mobile phone or computer. This client application allows visitors to browse the web and request specific resources. On the other hand, the server is the source from which the requested information is retrieved and served back to the client.
Client-side tracking tracks events and user interactions directly on the client (browser) side. These events include clicks, form submissions, page views, scrolling, etc. The data is typically sent asynchronously to a third-party analytics platform or server through techniques like pixel tracking or AJAX calls. However, server-side tracking tracks data by logging it on the server when requests are made, or actions are completed, making it less prone to client-side restrictions and ad blockers.
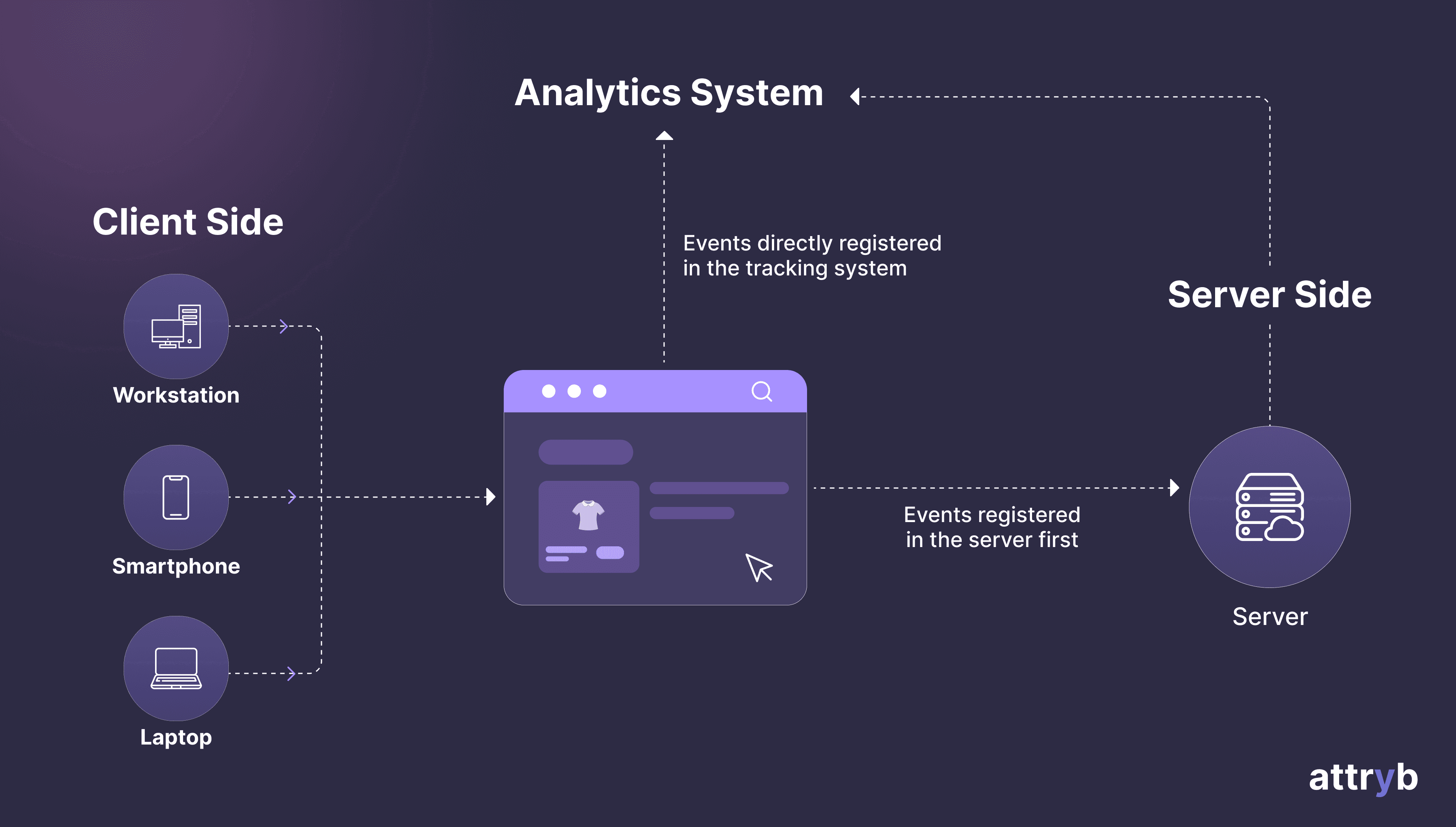
Figure 1. Client Side vs Server Side Tracking
What do businesses lose if they fail to track events correctly?
Ineffective event tracking causes businesses to lose visitor intelligence, impacting the performance of marketing campaigns.
Inaccurate Performance Measurement: Without correct event tracking, businesses do not have reliable data on metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and return on ad spend (ROAS). This leads to incorrect conclusions about the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Lower RoAS: Incorrect event tracking results in businesses paying for ads that do not generate the desired results. Without accurate data on which channels, ads, or keywords drive conversions, businesses may continue to invest in underperforming campaigns, leading to inefficient ad spending and poor return on investment.
Flawed Attribution: Event tracking is essential for proper attribution modelling. It determines how conversions are credited to different touchpoints in the customer journey. Inaccurate event tracking can lead to incorrect attribution, causing misguided marketing efforts and budget allocations.
Compliance & Legal Cost: In many regions, there are regulations and laws surrounding privacy and data collection, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Failing to track events correctly or violating user consent requirements can lead to legal consequences and hefty fines.
Gartner estimates a $12.9 M annual loss due to incomplete and inaccurate event tracking.
What’s the best path to correctly track events?
The combination of client-side and server-side tagging is the best and a clear choice. -
This combination approach offers advantages for businesses navigating the realm of web analytics. Client-side tagging provides agility and quick adjustments while server-side tagging enables control, privacy adherence and future-proof tracking in a cookie-less world. This collaboration translates into the following benefits:
Comprehensive Data Insights: The amalgamation of client-side and server-side tracking presents a pathway to fetch insights into user interaction. It limits the chance of missed events.
Enhanced Privacy and Compliance: Considering growing concerns over data privacy, the hybrid approach offers the best solution to visitor tracking. Server-side tagging reduces reliance on third-party scripts running in user browsers, mitigating privacy risks and aligning with regulatory frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA.
Optimized Performance: Organizations can optimize website performance and user experience by integrating client-side and server-side tagging. Offloading certain tracking and processing tasks to server-side environments alleviates the burden on user devices, leading to faster page load times and improved responsiveness across diverse browsing environments.
Flexibility and Scalability: Businesses can scale their analytics infrastructure and tailor tagging strategies to meet evolving business needs by fostering interoperability between client-side and server-side systems.
Pitfalls of the best approach i.e. tracking both Client and Server-Side Events
While combining the data from both the client and server side offers holistic data, the approach also creates issues such as event duplication. The platforms have built-in mechanisms to handle the deduplication of events. For example, in Meta Ads, advertisers implement the Conversions API alongside their Meta Pixel, causing event duplication from the client and server side. However, Meta uses a system to differentiate between distinct and overlapping events. For duplicate events, Meta matches the event name and event ID to de-duplicate the events before further processing, such as attribution, segment creation, and ad delivery.
With multiple data sources (client and server) and event processing logic (de-duplication logic) data freshness and completeness become an issue for tracking systems.
Data Freshness: refers to how recent the data is within the output of a data product. It typically refers to the time gap between when a pipeline extracted some source data and now. Data freshness is a concept than a specific metric so its measurement may vary depending on the context. Sending events in real-time or in batches based on a timeline (less than 1 hour) via the Conversions API ensures that they can be used for attribution and optimized for ad delivery. If you delay the submission of your events by more than 2 hours, it can substantially reduce the performance of ads optimized for those events. Events submitted with a delay of 24 hours or more may face challenges with attribution accuracy and optimized ad delivery.
Data Completeness: Missing data leads to statistically insignificant segments and poor conversion attribution. Businesses need to combine their visitor data with the platform data to provide a holistic picture of the visitor data. In Meta, businesses can pass their data through a unique visitor ID. This additional data will help in:
Scaling business: Once you provide a unique visitor ID, it can be used again across different channels and to create different audiences. On the business end, mapping the visitor ID to Meta’s external id will eliminate the need to manage large numbers of PIIs.
Improving match rates and leveraging matches across channels: Improving match rates on channels businesses do not have access to certain identifiers, leveraging information from another channel.
Creating audiences: The additional data helps businesses create segments at a granular level, improving the effectiveness of the audiences.
Increase security and privacy: Instead of uploading hashed PIIs multiple times, businesses can send visitor IDs with PIIs once and reuse that match.
Accurately tracking events is critically important for the success of performance marketing campaigns. By combining client and server-side event tracking, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and interactions across digital platforms. This hybrid approach offers enhanced data insights, improved privacy and compliance adherence, optimized website performance, and flexibility to adapt to evolving analytics needs. However, businesses must carefully navigate the potential pitfalls like event duplication, data freshness, and data completeness issues. They must Implement robust deduplication mechanisms, ensure timely event transmission, and leverage unique visitor identifiers to help mitigate these challenges. Ultimately, a well-executed event tracking strategy that harmonizes client and server-side data will empower businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimize marketing campaigns, and improve Return on Investment.
In data-driven marketing, the smallest trackable unit of visitor interaction is called an event. Events are user actions that are tracked, measured, and stored to evaluate the effectiveness of a performance marketing campaign. Combining multiple events across time helps businesses track user journeys across the website. Some of the common events tracked include:
Social Interactions: when users engage by sharing, liking or commenting on social media content related to the campaign
Impressions: when an advertisement is displayed to a visitor
Clicks: when a user clicks on an advertisement
Add to Cart: when a user adds a product to the shopping cart
Conversions: when a user takes a desired action like making a purchase or submitting a form
Once an event is identified and triggered, the tracking code sends the tracking data with metadata like event category, event name, timestamp, and other related attributes. The tracking of these events can occur either on the client side or the server side. While it may seem convenient to do everything on the client or the server side, there are drawbacks to both methods. The choice between client-side and server-side tracking depends on the type of events being tracked. One approach may be more suitable than the other based on needs. Also, while some of the events are available on the client side, issues like ad blockers make tracking events on the server a better option.
Client vs. server tracking: what’s the difference?
The client initiates requests for resources like files or web pages, acting as the consumer of information. Conversely, the server's responsibility is to respond to these requests by providing the requested data or content.
The client represents the user-facing application or interface, such as a web browser (Firefox, Chrome) running on a mobile phone or computer. This client application allows visitors to browse the web and request specific resources. On the other hand, the server is the source from which the requested information is retrieved and served back to the client.
Client-side tracking tracks events and user interactions directly on the client (browser) side. These events include clicks, form submissions, page views, scrolling, etc. The data is typically sent asynchronously to a third-party analytics platform or server through techniques like pixel tracking or AJAX calls. However, server-side tracking tracks data by logging it on the server when requests are made, or actions are completed, making it less prone to client-side restrictions and ad blockers.

Figure 1. Client Side vs Server Side Tracking
What do businesses lose if they fail to track events correctly?
Ineffective event tracking causes businesses to lose visitor intelligence, impacting the performance of marketing campaigns.
Inaccurate Performance Measurement: Without correct event tracking, businesses do not have reliable data on metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and return on ad spend (ROAS). This leads to incorrect conclusions about the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Lower RoAS: Incorrect event tracking results in businesses paying for ads that do not generate the desired results. Without accurate data on which channels, ads, or keywords drive conversions, businesses may continue to invest in underperforming campaigns, leading to inefficient ad spending and poor return on investment.
Flawed Attribution: Event tracking is essential for proper attribution modelling. It determines how conversions are credited to different touchpoints in the customer journey. Inaccurate event tracking can lead to incorrect attribution, causing misguided marketing efforts and budget allocations.
Compliance & Legal Cost: In many regions, there are regulations and laws surrounding privacy and data collection, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Failing to track events correctly or violating user consent requirements can lead to legal consequences and hefty fines.
Gartner estimates a $12.9 M annual loss due to incomplete and inaccurate event tracking.
What’s the best path to correctly track events?
The combination of client-side and server-side tagging is the best and a clear choice. -
This combination approach offers advantages for businesses navigating the realm of web analytics. Client-side tagging provides agility and quick adjustments while server-side tagging enables control, privacy adherence and future-proof tracking in a cookie-less world. This collaboration translates into the following benefits:
Comprehensive Data Insights: The amalgamation of client-side and server-side tracking presents a pathway to fetch insights into user interaction. It limits the chance of missed events.
Enhanced Privacy and Compliance: Considering growing concerns over data privacy, the hybrid approach offers the best solution to visitor tracking. Server-side tagging reduces reliance on third-party scripts running in user browsers, mitigating privacy risks and aligning with regulatory frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA.
Optimized Performance: Organizations can optimize website performance and user experience by integrating client-side and server-side tagging. Offloading certain tracking and processing tasks to server-side environments alleviates the burden on user devices, leading to faster page load times and improved responsiveness across diverse browsing environments.
Flexibility and Scalability: Businesses can scale their analytics infrastructure and tailor tagging strategies to meet evolving business needs by fostering interoperability between client-side and server-side systems.
Pitfalls of the best approach i.e. tracking both Client and Server-Side Events
While combining the data from both the client and server side offers holistic data, the approach also creates issues such as event duplication. The platforms have built-in mechanisms to handle the deduplication of events. For example, in Meta Ads, advertisers implement the Conversions API alongside their Meta Pixel, causing event duplication from the client and server side. However, Meta uses a system to differentiate between distinct and overlapping events. For duplicate events, Meta matches the event name and event ID to de-duplicate the events before further processing, such as attribution, segment creation, and ad delivery.
With multiple data sources (client and server) and event processing logic (de-duplication logic) data freshness and completeness become an issue for tracking systems.
Data Freshness: refers to how recent the data is within the output of a data product. It typically refers to the time gap between when a pipeline extracted some source data and now. Data freshness is a concept than a specific metric so its measurement may vary depending on the context. Sending events in real-time or in batches based on a timeline (less than 1 hour) via the Conversions API ensures that they can be used for attribution and optimized for ad delivery. If you delay the submission of your events by more than 2 hours, it can substantially reduce the performance of ads optimized for those events. Events submitted with a delay of 24 hours or more may face challenges with attribution accuracy and optimized ad delivery.
Data Completeness: Missing data leads to statistically insignificant segments and poor conversion attribution. Businesses need to combine their visitor data with the platform data to provide a holistic picture of the visitor data. In Meta, businesses can pass their data through a unique visitor ID. This additional data will help in:
Scaling business: Once you provide a unique visitor ID, it can be used again across different channels and to create different audiences. On the business end, mapping the visitor ID to Meta’s external id will eliminate the need to manage large numbers of PIIs.
Improving match rates and leveraging matches across channels: Improving match rates on channels businesses do not have access to certain identifiers, leveraging information from another channel.
Creating audiences: The additional data helps businesses create segments at a granular level, improving the effectiveness of the audiences.
Increase security and privacy: Instead of uploading hashed PIIs multiple times, businesses can send visitor IDs with PIIs once and reuse that match.
Accurately tracking events is critically important for the success of performance marketing campaigns. By combining client and server-side event tracking, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and interactions across digital platforms. This hybrid approach offers enhanced data insights, improved privacy and compliance adherence, optimized website performance, and flexibility to adapt to evolving analytics needs. However, businesses must carefully navigate the potential pitfalls like event duplication, data freshness, and data completeness issues. They must Implement robust deduplication mechanisms, ensure timely event transmission, and leverage unique visitor identifiers to help mitigate these challenges. Ultimately, a well-executed event tracking strategy that harmonizes client and server-side data will empower businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimize marketing campaigns, and improve Return on Investment.
Share:
Share:

Anil Bains
Founder and CEO
Founder and CEO of Attryb Tech. A seasoned entrepreneur who brings over a decade of experience to Attryb. He also loves traveling - 43 countries and counting - and used to be pretty good at Volleyball: he captained at Volleyball Nationals Under-17 team!
Founder and CEO of Attryb Tech. A seasoned entrepreneur who brings over a decade of experience to Attryb. He also loves traveling - 43 countries and counting - and used to be pretty good at Volleyball: he captained at Volleyball Nationals Under-17 team!
Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!

Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!

Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!

Get Started Today
Experience the power of personalization for increasing engagement and conversions Request a demo now!

Keep Reading
Load More




